Human Factors
Finite State Machines
Alloy Model Checking
A Formal Approach to the Analysis of Human-Machine Interaction with Fuzzy Mental Model Finite State Machines
Human Factors
Finite State Machines
Alloy Model Checking
Description
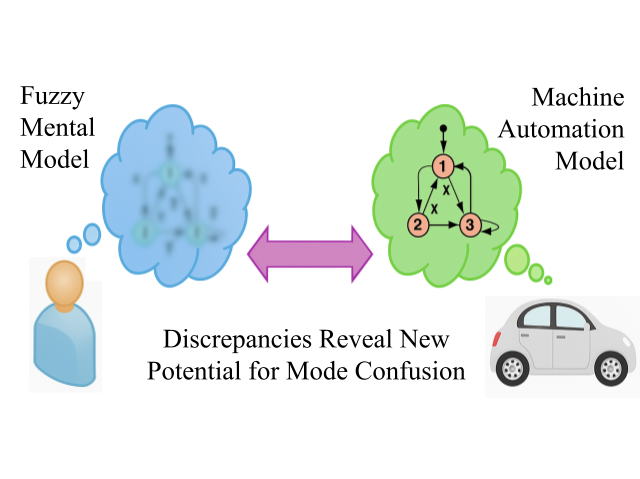
Human factors researchers have long argued that human use mental models to track the system’s state and predict its behaviors. Maintaining an accurate mental model is crucial for safe and effective human-machine interaction as misalignment between the model and the system, known as mode confusions, can result in automation surprises, where the system fails to act as expected. Thus, avoiding mode confusions has become vital in the design of safety-critical systems and human-centered applications.
The executable nature of mental models has prompted some researchers to view them as rudimentary programs that can be represented by state machines. However, state machines with a deterministic execution semantics fall short of accurately modeling mental models because they do not capture the vagueness of human reasoning. To overcome this limitation, researchers have introduced Fuzzy Mental Model Finite State Machines (FMMs), a new formalism designed to precisely capture the vagueness and imprecision of human mental models. It builds upon state machines but incorporate fuzzy logic to handle vagueness. Fuzzy logic, developed to reflect the inherent imprecision of human thinking and language, allows for categories to have degrees of membership from 0 (not at all) to 1 (completely) rather than falling into discrete categories like true or false.
This work investigates the potential of FMMs in formal analyses to facilitate the verification of safe and robust human-machine interactions, explicitly accounting for the vagueness inherent in mental models.
Publications: